The rise of chronic student absenteeism has been an dramatic trend over the past few years. According to the most recent federal data, 14.7 million students nationwide were marked as chronically absent during the 2020-2021 school year. That’s nearly double the 8 million students pre-pandemic who had missed over 10 percent of school days, signaling academic risk. Narrowing the focus further, chronic absenteeism in California rose to 30% during the 2021-2022 school year, more than doubling the level of absenteeism in 2018-2019.
With student absenteeism rates increasing exponentially in post-pandemic years, educators are focusing on student engagement and utilizing new strategies to reduce chronic absenteeism. These goals empower equal education opportunities across the board and maximize students’ academic, social, and professional potential.
Fortunately, strategies to lower chronic absenteeism have evolved alongside growing concerns. In this article, we will explore these five proven approaches to reducing student absenteeism in today’s schools.
What is Chronic Student Absenteeism? Why Does it Matter?
Chronic absenteeism is defined as students who have missed 15 days – or 10% – of school per calendar year, placing them at academic risk. Unlike truancy, absenteeism refers to any missed school days, excused and unexcused. Additionally, high levels of chronic absence are also more common among certain demographics than others. Consider access to transportation, access to technology during distance learning, household factors, and other elements that place students at a disadvantage for consistent attendance.
Once absenteeism becomes chronic, students are far more likely to fall behind one or more grade levels, contributing to higher dropout rates by the time students reach high school. Irregular attendance can also be linked to increased involvement in the criminal justice system, diminished health, and limited employment opportunities. In turn, low engagement places additional strain on teachers to address learning gaps and on school leaders to source funding and resource allocation for educational programs.
Absences can easily add up and lead to poor academic outcomes for students at all grade levels. To counteract this trend, community-based, targeted strategies are needed to prevent a pattern of student absenteeism from becoming the norm.
Understanding the Causes of Chronic Student Absenteeism
By far, the pandemic significantly shifted learning dynamics, causing learning losses and absenteeism due to rolling school closures, staff shortages, and quarantines.
The pandemic also intensified other issues for chronic student absenteeism, including economic challenges at home, health concerns, misbehavior, as well as a lack of engagement and belonging within schools. In addition, students can regularly miss school when faced with transportation obstacles, housing and food security, responsibilities at home, and lack of access to necessary tools to succeed.
Recognizing these challenges equips educators with the knowledge to strategically reduce chronic absenteeism in today’s students.
5 Researched-Based Strategies for Schools
Home Visits
Empowering students in academic success takes a community. Home visits are a powerful way for educators and school administrative staff to foster stronger relationships with families. Implementation might take the form of a district-wide initiative or a targeted intervention for chronically absent students.
A 2022 study by LEAP on the effectiveness of home visits identified several factors that made home visits most effective. Delivering personalized, dynamic support was a leading element for success. Other key factors included the home visitor’s fluency in the language used at home, the degree of collaboration between staff and families, and actionable plans to re-engage at-risk students.
Ultimately, the results of the evaluation demonstrated a significant increase in attendance rates for students who received home visits. In addition, family-school relationships improved, and students felt an increased sense of belonging.
School Transportation Logistics
Ease and accessibility to transportation don’t just ensure that students can logistically get to school on time. It also plays a crucial role in alleviating school anxiety and discouragement, especially for those lacking appropriate resources.
A study by Bloomberg noted that a simple one-minute increase in commute time resulted in a 1.3-minute decrease in sleep. This may not sound significant, but consider a 15-minute commute that results in 20 minutes less sleep for a student. Transportation inequity has been linked to increased absenteeism, especially for students who face a commute of 45 minutes or more.
Educational boards can contribute to ensuring equal access and opportunity to learning by improving school bus efficiency. Some cities, such as Boston for example, have made changes to their bus system’s routes and timetables. By using algorithmic bus routing, they drive efficiency while supporting students who live more than 30 minutes outside of school districts. These small changes can result in a positive overall impact on student attendance.
Welcoming Environment
Creating an environment of belonging is a powerful tool in reducing chronic student absenteeism. One study considered the impact of “Positive Greetings at the Door (PGD)” on overall student welfare. This included one-on-one time with students and parents, increased social and extracurricular engagement, and, most importantly, welcoming students at the door each morning.
When done consistently, the simplest gestures can have the greatest impact. The PGD model is just one example that can cultivate an inclusive and inviting classroom that students want to come back to.
Tiered Interventions
Taking a proactive approach at each stage of a student’s attendance journey gives educators a better pulse on engagement. Experts suggest tiered interventions as an effective response to absenteeism.
Tier 1 addresses students who have missed less than 10% of attendance. It includes foundational practices for positive learning conditions, such as recognition of good attendance or engagement, personalized family communication regarding absences, and clear expectation settings.
Tier 2 prompts a deeper investigation into rising absenteeism, addressing factors like transportation and home life concerns with early intervention. Tactics include expanded tutoring support, home visits, and arrangements with community services for family needs.
At Tier 3, educators may work collaboratively with appropriate agencies to ensure student welfare. In this stage, comprehensive absentee data is vital in determining the best course of action. Educators must ensure data accuracy at each tier of the process to determine intensive interventions, whether they involve legal intervention or individualized learning plans.
Technology Solutions
Studies show that evidence-based interventions work best for improving attendance rates amid increasing chronic absenteeism. By using technology to capture attendance data over time, schools can quickly and easily identify, report, and develop targeted interventions for chronically absent students.
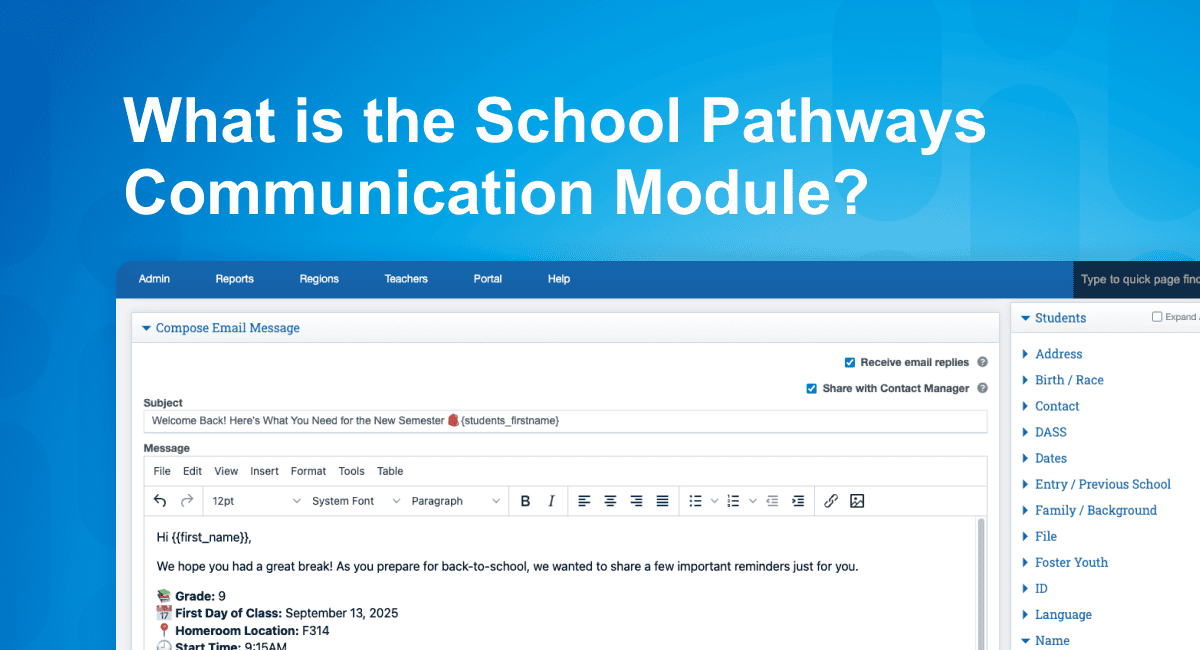
When it comes to improving student outcomes, using a Student Information System (SIS) is essential to help educators generate reports and see trends over time based on real-time attendance data. These insights help create a coordinated approach to support student needs with the necessary services, resources, or family involvement. A well-implemented platform can also adapt to non-traditional learning programs to track real-time student engagement data in hybrid or online learning environments.
Support Stronger Student Engagement with Proven Strategies
Creating a space for learning means meeting every student where they are. These five research-backed strategies for reducing chronic student absenteeism can elevate your organization’s engagement while empowering success for every learner.
School Pathways is committed to supporting students in reaching their full potential by empowering educators and administrators with the plans, content, tools, and data they need to overcome unique education challenges. If you’re ready to see how our Student Information System and Personalized Learning System help schools tackle student engagement and activity, schedule a demo with us. We’d love to chat!